Empowering Gardeners with the Secrets to Soil Success
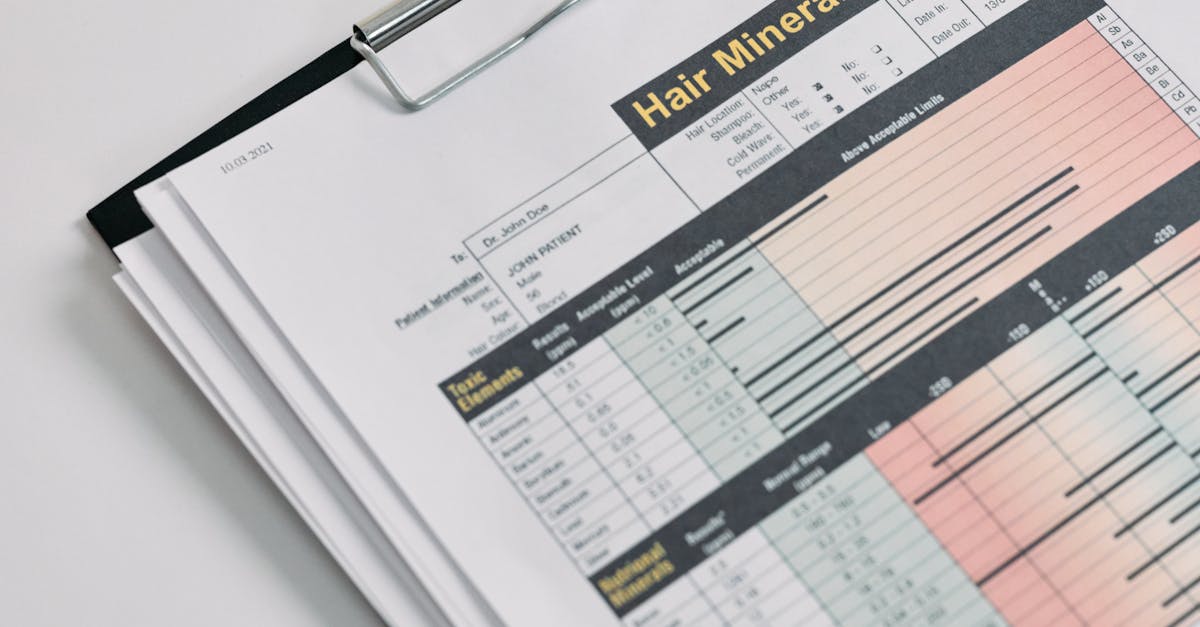
Unlocking the Secrets of Soil Test Reports: A Journey to Soil Health and Plant Prosperity
Step into the world of soil testing and discover the hidden gems that can transform your gardening game. Soil test reports are not just pieces of paper; they are treasure maps leading to a flourishing garden. This comprehensive guide will decipher each section of your soil test report like a pro, empowering you to understand your soil’s needs and make informed decisions for its wellbeing. Prepare to witness the transformation of your soil into a thriving hub of nutrients, where plants flourish and nature rejoices.
Embark on this exciting journey of soil exploration, and let’s delve into the fascinating world of soil testing, armed with the knowledge to interpret your soil test reports like a seasoned expert. Get ready to cultivate a thriving garden, one soil test at a time.
Key Insights
- Understanding your soil test report is crucial for optimizing plant growth.
- Soil pH level significantly impacts nutrient availability, so it’s essential to maintain the right balance for your plants.
- Macronutrients (N-P-K) and micronutrients (Ca-Mg-S) play vital roles in plant health, and addressing deficiencies is key.
- Soil texture and organic matter influence water retention, drainage, and fertility, so improving these aspects enhances soil health.
- Troubleshooting common soil issues like nutrient imbalances, pH problems, drainage problems, and compaction ensures a thriving environment for your plants.
1. Deciphering Soil Test Reports: A Comprehensive Breakdown
Deciphering Soil Test Reports: A Comprehensive Breakdown
Unveiling the secrets of your soil test report is like embarking on a treasure hunt for your garden’s success. Each result holds valuable clues to your soil’s health and the key to unlocking its full potential. Let’s dive into each section of your report and decipher the hidden messages it holds:
- pH Level: Imagine pH as the soil’s mood. A balanced pH level, like a happy medium, ensures nutrients are readily available for your plants to thrive. Understanding your soil’s pH is crucial for creating an environment where your plants can flourish.
- Macronutrients (N-P-K): Meet the power trio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, the heavy hitters in the nutrient world. They form the foundation of plant growth, influencing everything from lush foliage to bountiful harvests. Getting their levels just right is like giving your plants a superhero boost.
- Micronutrients (Ca-Mg-S): While they may play a supporting role, micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are the unsung heroes of soil health. They may be present in smaller amounts, but their impact is mighty, ensuring strong roots, sturdy stems, and vibrant blooms.
2. Step 1: Understand Your Soil’s pH Level
Step 1: Understand Your Soil’s pH Level
Picture your soil’s pH level as a sliding scale, with 7 being neutral. When the pH dips below 7, your soil becomes acidic, and above 7, it’s alkaline. This seemingly simple number holds the key to unlocking a world of nutrient availability for your plants.
Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, around 6.0 to 7.0. In this sweet spot, nutrients are most readily absorbed and utilized by your leafy friends. However, some plants, like blueberries and rhododendrons, thrive in more acidic soils, while others, such as alfalfa and asparagus, prefer alkaline conditions.
Knowing your soil’s pH level empowers you to make informed decisions about amendments. If your soil is too acidic, you can add lime to raise the pH, and if it’s too alkaline, you can add sulfur to lower it. By adjusting the pH, you create an environment where your plants can flourish and reach their full potential.
3. Step 2: Analyze Macronutrients (N-P-K)
Step 2: Analyze Macronutrients (N-P-K)
Let’s meet the dynamic trio of macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These nutrients are the foundation upon which茁壮 growth is built, influencing everything from lush foliage to bountiful harvests.
- Nitrogen (N): Think of nitrogen as the protein powerhouse for your plants. It’s responsible for producing chlorophyll, the green pigment that allows plants to harness sunlight and create their own food. Nitrogen deficiency can lead to stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Phosphorus (P): Picture phosphorus as the energy booster for your plants. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, root development, and seed production. A lack of phosphorus can result in weak stems and poor flowering.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is the guardian of water balance and nutrient transport within plants. It helps regulate water uptake and movement, and supports disease resistance. Potassium deficiency can manifest as brown or yellow leaf edges and reduced fruit quality.
Understanding the optimal levels of these macronutrients and addressing any deficiencies is key to unlocking the full potential of your garden. Soil test reports provide valuable insights into your soil’s nutrient profile, empowering you to make informed decisions about fertilization and soil amendments.
4. Step 3: Examine Micronutrients (Ca-Mg-S)
Step 3: Examine Micronutrients (Ca-Mg-S)
While micronutrients may be required in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients, their importance cannot be understated. Calcium, magnesium, and sulfur play vital roles in plant health and contribute to茁壮 growth.
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium acts as the skeletal system for plants, strengthening cell walls and promoting root development. It also aids in nutrient uptake and reduces the risk of blossom-end rot in fruits and vegetables.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is the heart of chlorophyll, the green pigment that fuels photosynthesis. It also contributes to seed production and helps plants withstand stress.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is a component of proteins and enzymes, and it supports nitrogen metabolism and photosynthesis. It also enhances seed quality and flavor in some crops.
Ensure the presence of these micronutrients in your soil by regularly testing and amending accordingly. Organic matter, such as compost and manure, is a rich source of micronutrients and can help improve soil health overall.
5. Step 4: Interpreting Soil Texture and Organic Matter
Step 4: Interpreting Soil Texture and Organic Matter
Soil texture and organic matter play crucial roles in the overall health and productivity of your garden. Understanding their impact and implementing measures to improve them can significantly enhance plant growth.
- Soil Texture: Soil texture refers to the proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in your soil. Each texture has unique characteristics that influence water retention, drainage, and aeration.
- Sandy soils drain quickly and warm up early in the season, but they tend to be low in nutrients and water retention.
- Silty soils have a smooth, flour-like texture and hold water and nutrients well, but they can be prone to compaction.
- Clay soils have high water retention capacity and are rich in nutrients, but they can be slow to drain and difficult to work with.
- Organic Matter: Organic matter, such as compost, manure, and plant debris, is the lifeblood of healthy soil. It improves water retention, drainage, aeration, and nutrient availability. It also supports beneficial soil organisms and enhances the overall soil structure.
By understanding your soil texture and organic matter content, you can make informed decisions about soil amendments and management practices to create an optimal environment for your plants.
6. Step 5: Troubleshooting Common Soil Issues
Step 5: Troubleshooting Common Soil Issues
Soil problems are a part of every gardener’s journey, but with the right knowledge, you can rectify these issues and restore your soil’s health.
- Nutrient Imbalances: Nutrient deficiencies or excesses can occur due to various factors. By understanding the symptoms and causes of each nutrient imbalance, you can make informed decisions about soil amendments and fertilization practices.
- pH Problems: Soil pH that is too acidic or alkaline can hinder nutrient availability and plant growth. Soil amendments, such as lime or sulfur, can be used to adjust pH levels and create a more favorable environment for plants.
- Drainage Problems: Poor drainage can lead to waterlogged soil, which can suffocate roots and promote disease. Improving drainage through techniques like raised beds or installing drainage tiles can alleviate these issues.
- Compaction: Compacted soil can restrict root growth and water infiltration. Aeration practices, such as tilling or using a garden fork, can help break up compacted soil and improve its structure.
By identifying and addressing common soil issues, you can create a thriving environment for your plants and enjoy a bountiful harvest.
How often should I get my soil tested?
It’s generally recommended to test your soil every 3-4 years, or more frequently if you have made significant changes to your garden or if you are experiencing plant growth problems.
What is the best way to collect a soil sample for testing?
Collect soil samples from several different locations in your garden and combine them into one composite sample. Dig down to a depth of about 6 inches and collect about 1 cup of soil from each location. Avoid sampling from areas where fertilizers or manure have been recently applied.
What if my soil test results show that my soil is deficient in a particular nutrient?
If your soil test results show that your soil is deficient in a particular nutrient, you can add that nutrient to your soil through fertilizers or compost. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package carefully to avoid over-fertilizing.
How can I improve the organic matter content of my soil?
You can increase the organic matter content of your soil by adding compost, manure, or other organic materials. These materials will help to improve soil structure, water retention, and fertility.
What are some common soil problems and how can I fix them?
Some common soil problems include compaction, poor drainage, and pH imbalances. Compacted soil can be loosened by tilling or aerating. Poor drainage can be improved by adding organic matter or installing drainage tiles. pH imbalances can be corrected by adding lime or sulfur to the soil.
Table of Key Insights
| Key Insight | Description | |—|—| | Understanding Soil Test Reports | Decipher the sections of your soil test report to gain valuable insights into your soil’s health and nutrient profile. | | Maintaining Optimal pH Level | Soil pH greatly influences nutrient availability, so adjust it accordingly to create a favorable environment for plant growth. | | Balancing Macronutrients and Micronutrients | Macronutrients (N-P-K) and micronutrients (Ca-Mg-S) are essential for plant health. Address any deficiencies to optimize growth. | | Enhancing Soil Texture and Organic Matter | Soil texture and organic matter impact water retention, drainage, and fertility. Improve these aspects to promote soil health. | | Troubleshooting Common Soil Issues | Identify and resolve common soil problems, such as nutrient imbalances, pH problems, drainage issues, and compaction, to maintain a thriving soil environment. |
